Introduction
As RF power amplifiers continue to deliver higher output power in increasingly compact designs, thermal management has become a key challenge for system designers. Accurate prediction of junction temperature is essential to ensure reliability, maintain performance, and operate devices safely within their specified limits. For ART LDMOS RF power transistors, compact RC thermal networks offer a practical and efficient way to model both steady state and transient thermal behavior directly in circuit and system level simulations.
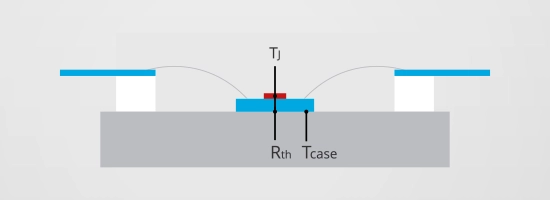
Whenever an RF transistor dissipates power, heat is generated at the junction and flows through the die, package, and mounting interface to the ambient environment. The resulting temperature rise depends not only on the amount of power but also on how quickly that power is applied.
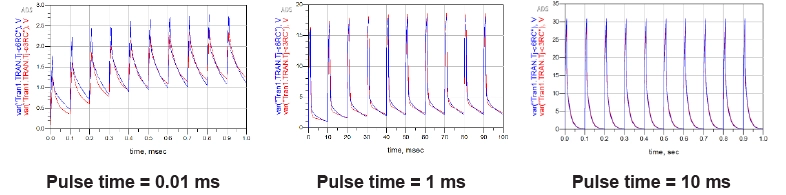
Transient thermal impedance captures this time dependent behavior. Short RF bursts can be tolerated at higher peak power levels because the device temperature rises more slowly, while continuous wave operation is governed by steady state thermal resistance. RC thermal models translate this measured behavior into simulation ready networks that accurately reproduce temperature rise over time.
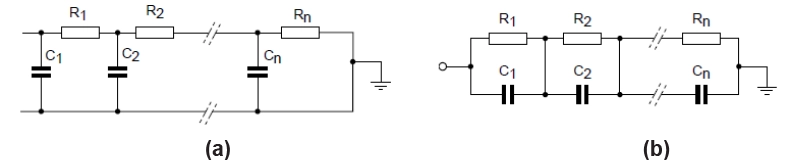
Two RC network representations are commonly used to model ART LDMOS devices.
The Foster model provides a compact mathematical fit to measured thermal impedance data and is well suited for quick transient analysis. It is easy to implement but does not reflect the physical structure of the device.
The Cauer model mirrors the physical heat flow path through the transistor by representing individual thermal layers with a ladder network. This makes it ideal for system level simulations, where the device model can be connected directly to PCB, interface material, or heatsink thermal networks.
Pulsed radar transmitters
In pulsed radar applications, RF power transistors operate with very high peak power and low duty cycles. Using RC thermal models, designers can accurately estimate junction temperature rise during each pulse and verify that the device remains within thermal limits, even under worst case operating conditions.
5G and cellular base stations
Modern cellular infrastructure often operates under dynamic load conditions with varying modulation and power levels. Electro thermal simulations using RC thermal networks allow designers to evaluate how self heating affects gain, efficiency, and linearity over time, supporting more robust amplifier designs.
Industrial RF heating and plasma systems
In industrial RF systems, long bursts or quasi continuous operation are common. By combining the internal Cauer model of an ART LDMOS device with external thermal networks representing the PCB and cooling solution, engineers can assess the complete thermal stack and optimize heatsink and airflow design.
Aerospace and defense electronics
Harsh environments and limited cooling options place strict demands on thermal reliability. Compact RC thermal models enable accurate system level simulations without excessive computational complexity, supporting reliable operation across wide temperature ranges.
By integrating compact RC thermal networks into electrical, electro thermal, or system level simulations, designers gain early insight into temperature behavior under realistic operating conditions. This approach reduces design risk, shortens development cycles, and supports thermally optimized RF power amplifier solutions.
ART LDMOS RC thermal models provide a proven foundation for designing high power RF systems that meet today’s demanding performance and reliability requirements.
About the author
Amir is a thermal modeling and characterization expert at Ampleon. He provides technical support to ensure products maintain optimal thermal performance and reliability over their lifetime.

Principal Thermal Engineer
Committed to your success
During the entire process from design to delivery, we provide a range of support options to address your needs. Whether you require load-pull data, application boards, samples, ADS / AWR models, assistance with a complex design challenge or seek quick advice, we are on stand-by to support you. Our application engineering resources are spread around the globe, with our offices in Nijmegen / The Netherlands, Toulouse / France, Smithfield / USA, and Shanghai / China.
This tool provides reliable lifespan data, shown as Median-Time-To-Failure (MTF) based on Junction Temperature (TJ), assuming electromigration as the primary wear-out mechanism.
This tool provides real-time and precise data calculations for Junction Temperature, Thermal Resistance, Minimum Efficiency, and Thermal Efficiency.
Ampleon's ART transistors are specifically engineered to deliver the best in terms of RF power, gain and efficiency, but more importantly, they boast crucial ruggedness and reliability features that set them apart from the competition.